Quick Start Guide¶
Now that Rayforge is installed and your machine is configured, let's run your first laser job! This guide will walk you through importing a design, configuring operations, and sending G-code to your machine.
Workflow Overview¶
flowchart LR
A[Import Design] --> B[Position & Scale]
B --> C[Assign Operation]
C --> D[Preview G-code]
D --> E[Generate G-code]
E --> F[Frame Job]
F --> G[Start Job]
style A fill:#e1f5ff
style C fill:#fff3e0
style D fill:#f3e5f5
style G fill:#e8f5e9Step 1: Import a Design¶
Rayforge supports various file formats including SVG, DXF, PDF, and raster images (JPEG, PNG, BMP).
- Click File → Open or press Ctrl+O
- Navigate to your design file and select it
- The design will appear on the canvas
Don't have a design yet?
You can create simple shapes using the canvas tools or download free SVG files from sites like Flaticon or SVG Repo.
Step 2: Position Your Design¶
Use the canvas tools to position and adjust your design:
- Pan: Middle-click and drag, or hold Space and drag
- Zoom: Scroll wheel, or Ctrl++ / Ctrl+-
- Move: Click and drag your design
- Rotate: Select the design and use the rotation handles
- Scale: Select the design and drag the corner handles
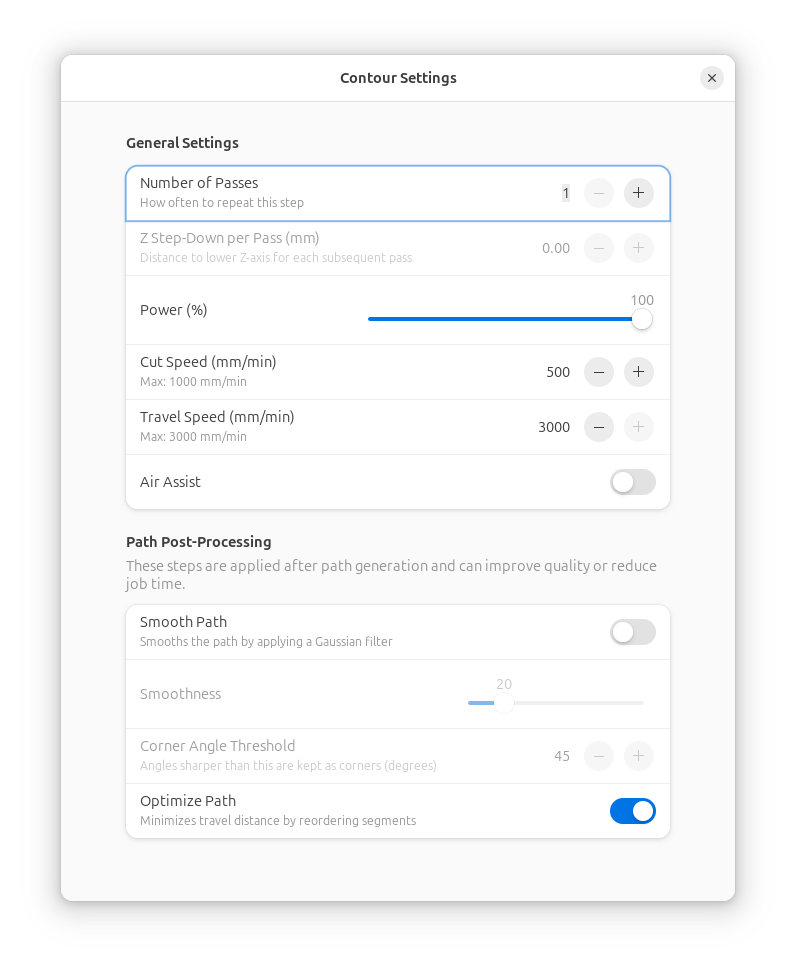
Step 3: Assign an Operation¶
Operations define how Rayforge will process your design. Common operations include:
- Contour: Cut along the outline of shapes
- Raster Engrave: Fill shapes with back-and-forth lines (for engraving)
- Depth Engrave: Create 3D depth effects from images
Adding an Operation¶
- Select your design on the canvas
- Click Operations → Add Operation or press Ctrl+Shift+A
- Choose the operation type (e.g., "Contour" for cutting)
- Configure the operation settings:
- Power: Laser power percentage (start low and test!)
- Speed: Movement speed in mm/min
- Passes: Number of times to repeat the operation (useful for cutting thick materials)
Start with Low Power
When working with new materials, always start with lower power settings and run test cuts. Gradually increase power until you achieve the desired result.
Material Testing Recommendations¶
| Material | Power (%) | Speed (mm/min) | Passes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | 10-20 | 3000-5000 | 1 |
| Cardboard | 30-50 | 1500-3000 | 1-2 |
| Plywood (3mm) | 60-80 | 300-600 | 1-3 |
| Acrylic (3mm) | 70-90 | 200-400 | 1-2 |
These are starting points only. Always test with your specific machine and materials.
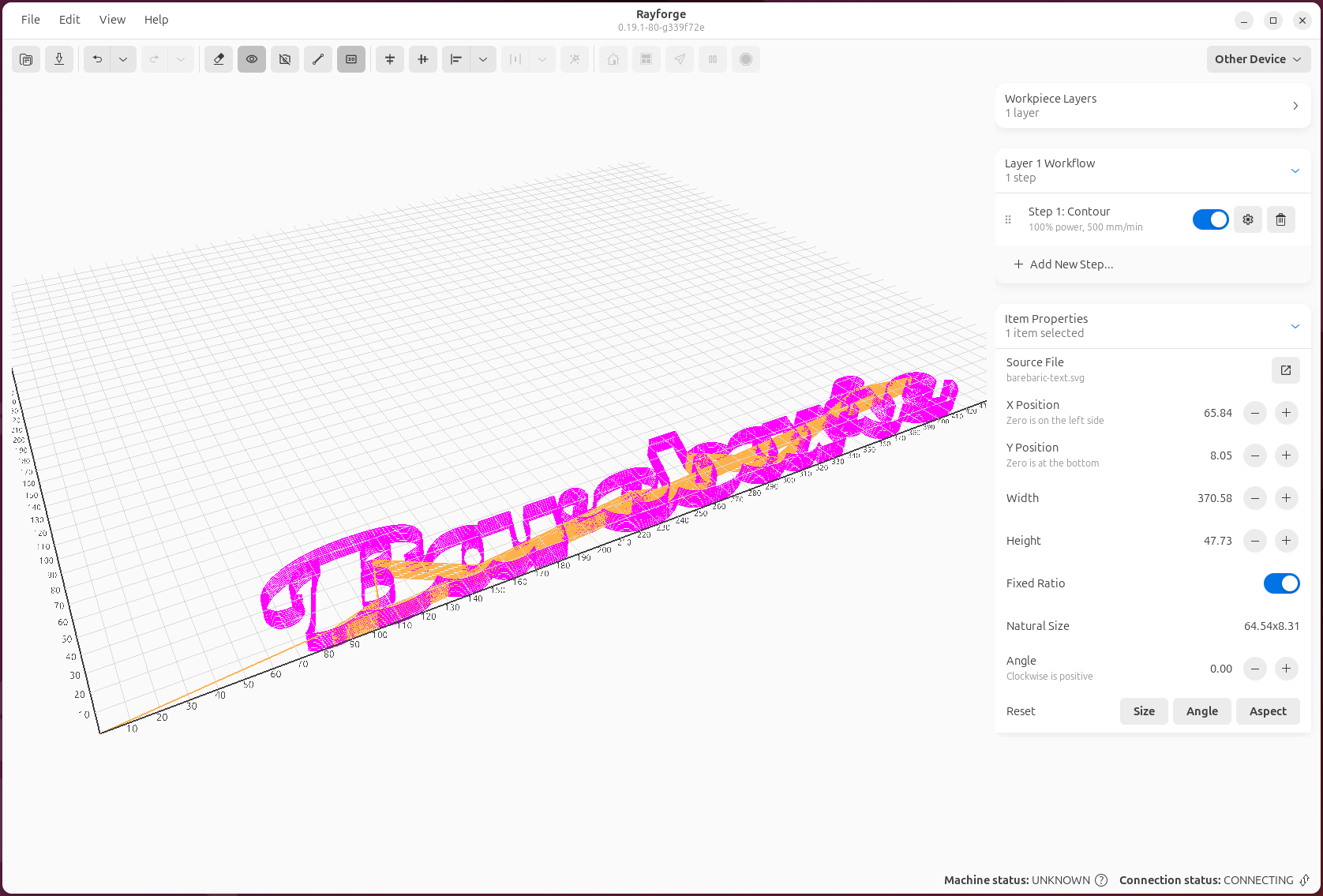
Step 4: Preview G-code¶
Before sending to your machine, preview the toolpath in 3D:
- Click View → 3D Preview or press Ctrl+3
- The 3D preview window shows the complete toolpath
- Use your mouse to rotate and zoom the preview
- Verify that the path looks correct
Catch Errors Early
The 3D preview helps you spot issues like:
- Missing paths
- Incorrect ordering
- Operations applied to the wrong objects
- Paths that exceed your working area
Step 5: Generate G-code¶
- Click Machine → Generate G-code or press Ctrl+G
- Rayforge will process your operations and generate the G-code
- The generated code appears in the G-code viewer
Step 6: Send to Machine¶
Safety First
- Ensure the work area is clear
- Never leave the machine unattended during operation
- Have fire safety equipment nearby
- Wear appropriate eye protection
Preparing Your Material¶
- Place your material on the laser bed
- Focus the laser according to your machine's instructions
- If using the camera, align your design using the camera overlay
Starting the Job¶
- Position the laser: Use the jog controls to move the laser to the starting position
- Click Machine → Jog Controls or press Ctrl+J
- Use the arrow buttons or keyboard arrows to move the laser
-
Press Home to home the machine
-
Frame the design: Run the framing function to verify placement
- Click Machine → Frame Job or press Ctrl+F
- The laser will trace the bounding box of your design at low/no power
-
Verify it fits within your material
-
Start the job: Click Machine → Start Job or press Ctrl+R
- Monitor the progress in the status bar
During the Job¶
- The right section of the status bar shows the current progress and total execution time estimate
- You can pause the job with Ctrl+P or click the Pause button
- Press Esc or click Stop to cancel the job (emergency stop)
Step 7: Finishing Up¶
Once the job completes:
- Wait for the exhaust fan to clear any fumes
- Carefully remove your finished piece
- Clean the laser bed if necessary
Congratulations!
You've completed your first Rayforge job! Now you can explore more advanced features.
Next Steps¶
Now that you've completed your first job, explore these features:
- Multi-Layer Operations: Assign different operations to layers
- Holding Tabs: Keep cut pieces in place during cutting
- Camera Integration: Use a camera for precise alignment
- G-code Macros: Automate repetitive tasks
Tips for Success¶
- Save your work: Use Ctrl+S to save your project frequently
- Test cuts: Always run a test cut on scrap material first
- Material database: Keep notes on successful power/speed settings for different materials
- Maintenance: Keep your laser lens clean and check belt tension regularly
- Air assist: If your machine has air assist, use it to prevent charring and improve cut quality
Need Help? Check the Troubleshooting section or visit the GitHub Issues page.